Azure AI Foundry is Microsoft’s end-to-end platform designed for building and deploying AI solutions in the cloud. This guide will walk you through the process of creating an AI Hub in the Azure portal, explore its capabilities, and discuss its use cases.
What is Azure AI Foundry?
Azure AI Foundry provides a unified environment for data scientists, developers, and business professionals to collaborate and create AI-powered applications. With its drag-and-drop interfaces, automated machine learning, and advanced AI services, it simplifies the AI development process.
Key Capabilities of Azure AI Foundry
1. Library of AI Models and Services
Azure AI Foundry acts as an umbrella that includes marketplaces for large language models from OpenAI, Meta, and various open-source models. It also offers APIs for advanced AI services such as Vision, Speech, and Document Intelligence.
2. Platform to Build AI Applications
Previously known as Azure AI Studio, Azure AI Foundry offers all necessary tools for building sophisticated AI applications. It supports orchestration, endpoints, custom functions, data indexing, and more.
Creating an AI Hub in Azure Portal
Note: Azure AI Foundry operates on a pay-as-you-go model. Ensure to check the pricing before use.
- Access Azure Portal:
- Go to the Azure portal.
- Search for “Azure AI Foundry” and click on it.
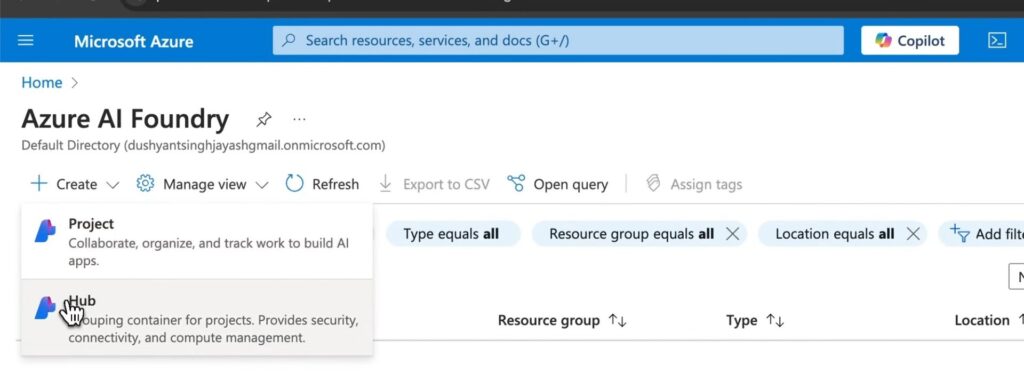
- Create an AI Hub:
- Click on “Create.”
-
- Choose between creating a project or a Hub.
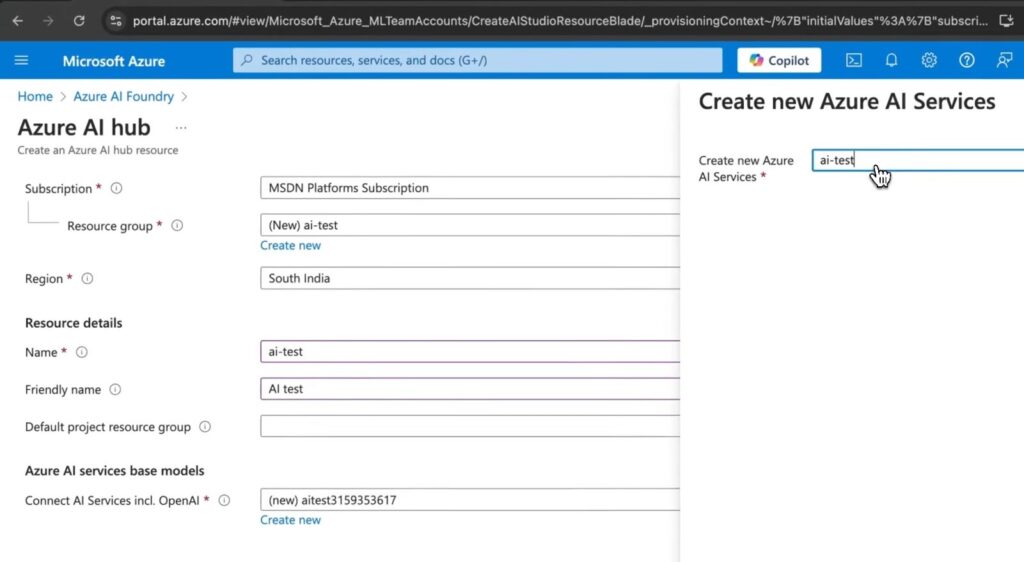
- Provide necessary details like Resource Group, Region, and Friendly Name.
-
- Connect AI services, including OpenAI.
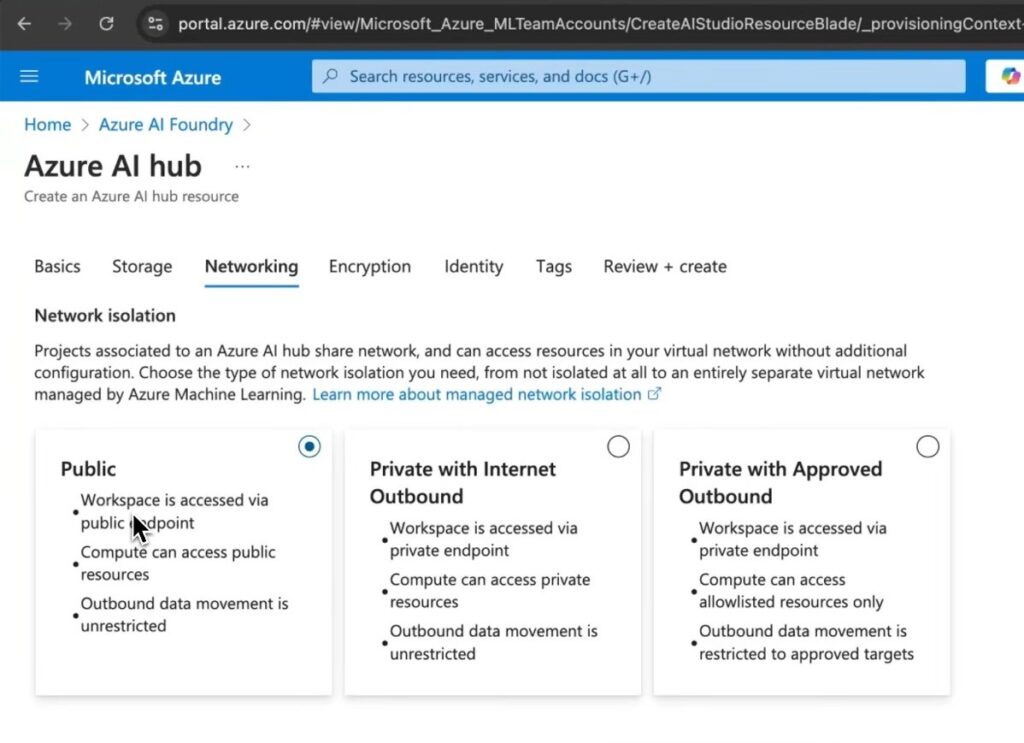
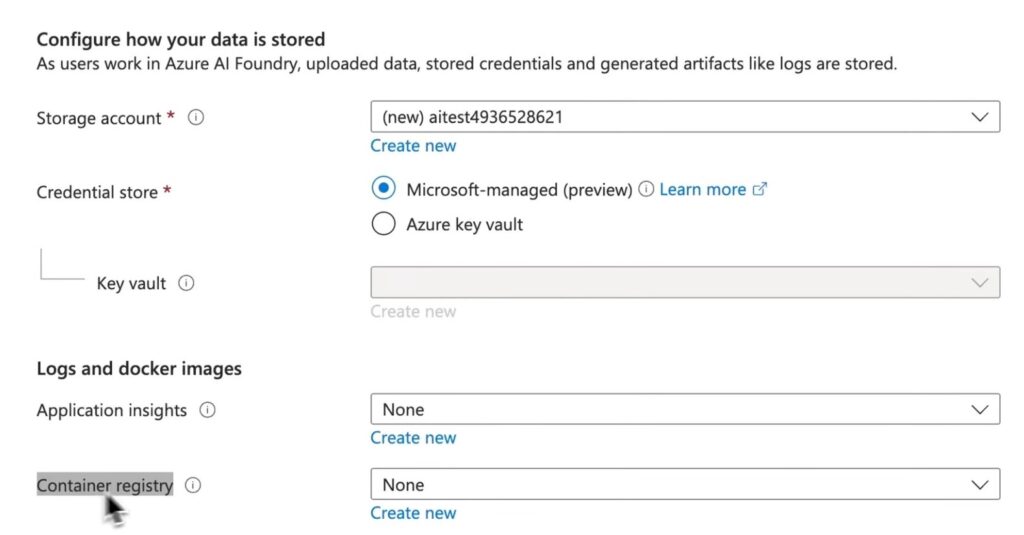
- Configure storage, networking (public, private with internet-bound, or private with approved outbound), encryption, and identity settings.
-
- Review and click “Create.”
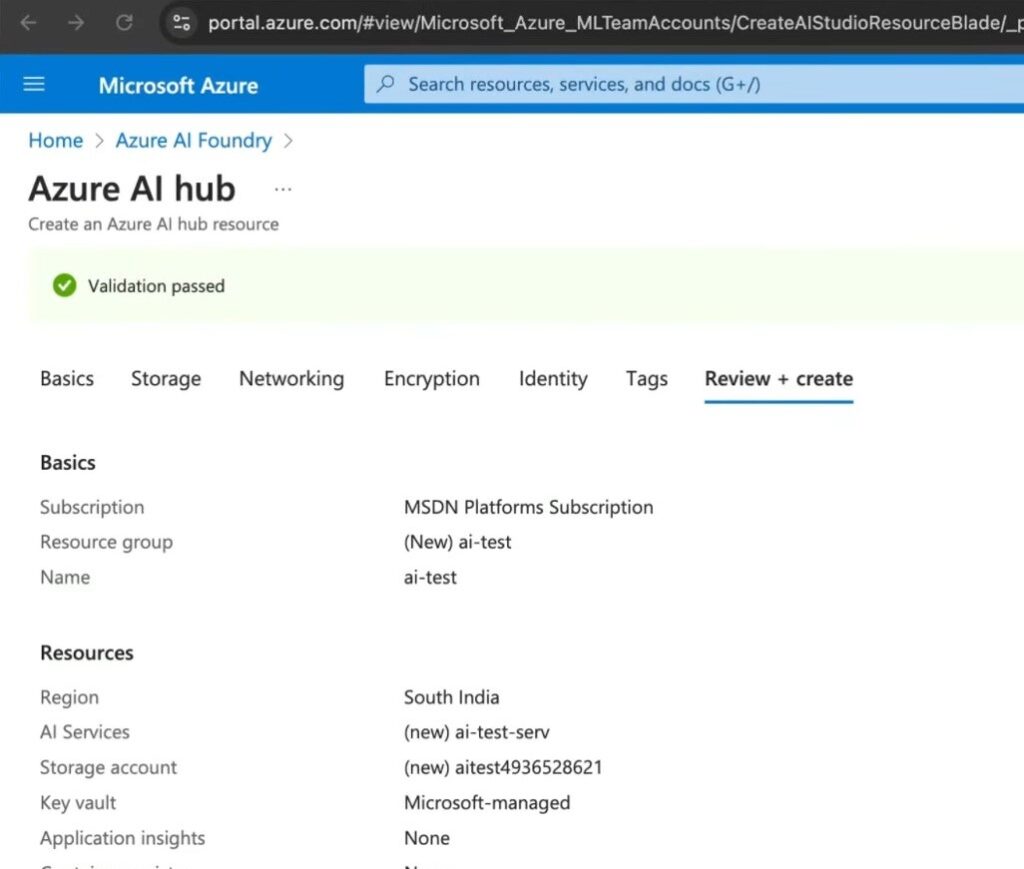
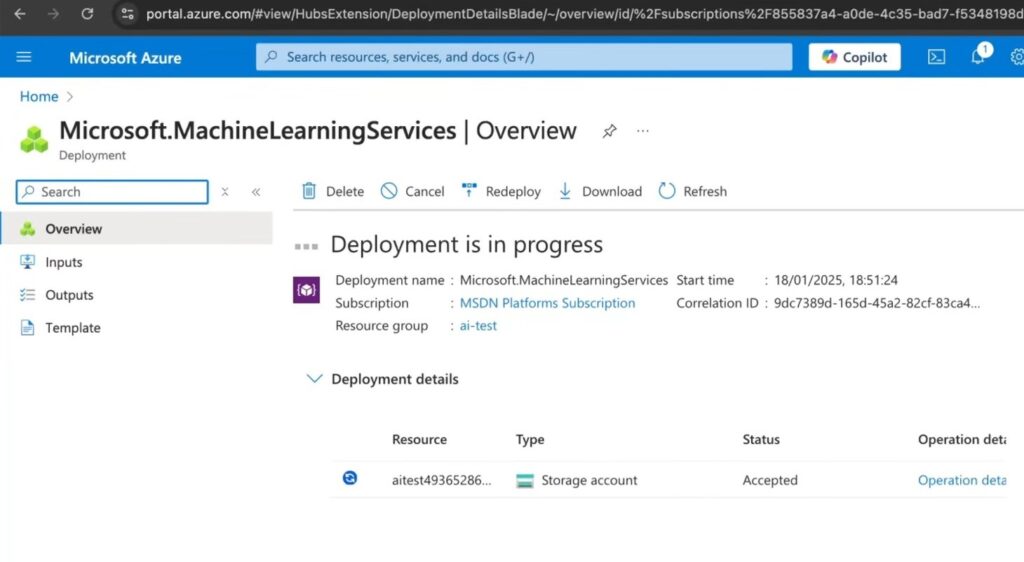
- Deployment:
- Wait for the deployment to complete.
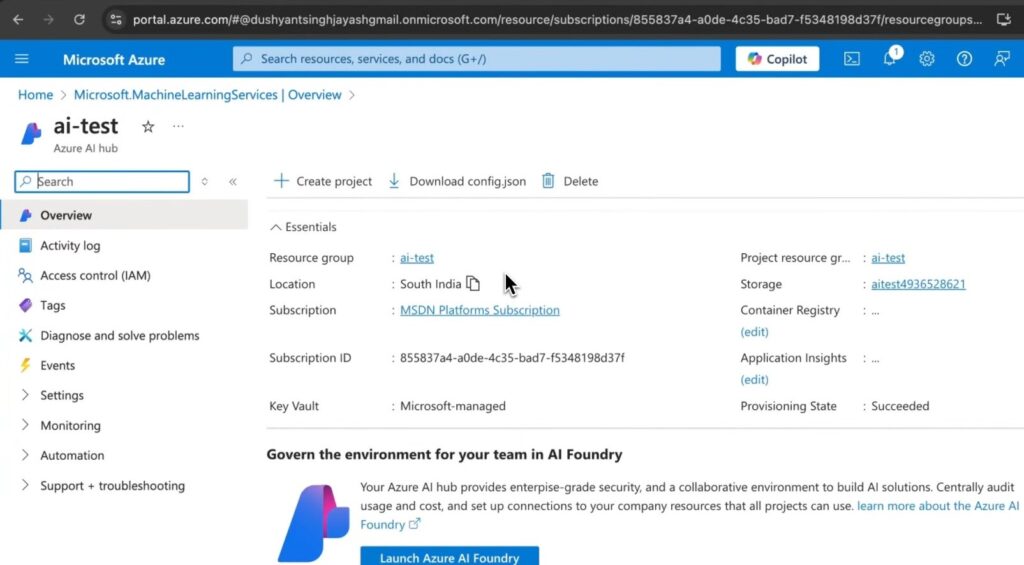
-
- Access the AI Hub through the provided endpoint.
Networking Options in Azure AI Foundry
- Public: Access via public endpoint with unrestricted outbound data movement.
- Private with Internet Outbound: Access via private endpoint with unrestricted outbound data.
- Private with Approved Outbound: Access via private endpoint with restricted outbound data to approved targets.